© ROOT-NATION.com - Use of content is permitted with a backlink.
Today, we’ll take a closer look at the capabilities of the AGM-158 JASSM air-launched cruise missile, developed by Lockheed Martin.
Recent reports suggest that the United States is nearing an agreement to supply Ukraine with long-range JASSM cruise missiles. Specifically, this refers to the AGM-158 JASSM, an air-launched precision weapon. The potential deployment of JASSM missiles to Ukraine could significantly alter the strategic dynamics of the conflict, as much of Russia’s territory would fall within the range of these highly accurate and powerful munitions.
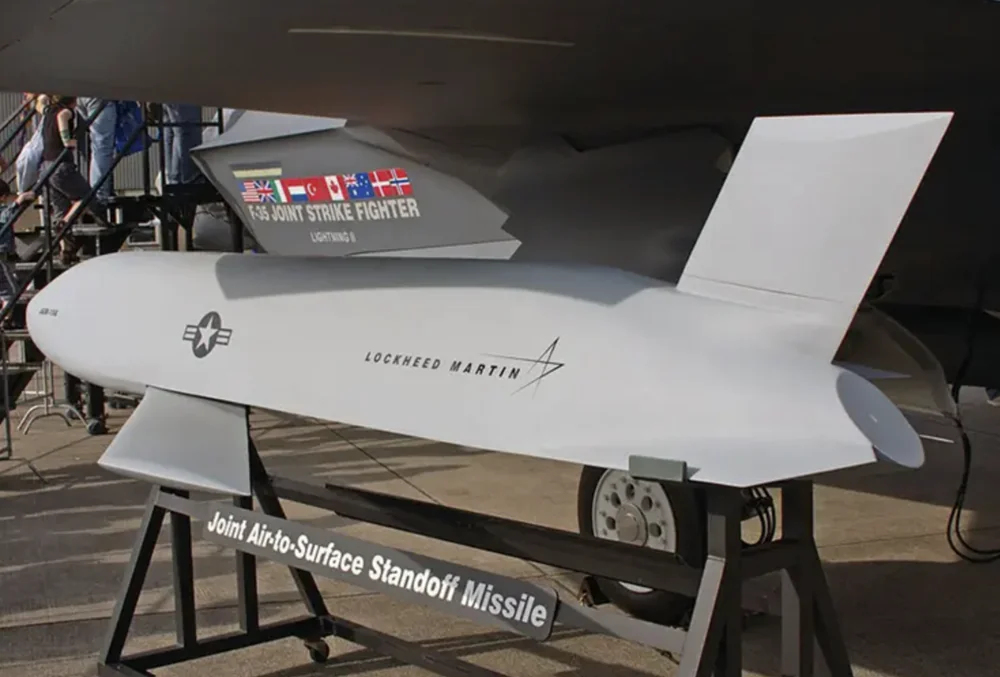

However, Ukraine’s Air Force may need to wait several months as the U.S. addresses technical considerations before any deliveries can take place.
In the meantime, we decided to take a closer look at these highly capable long-range cruise missiles and explore what makes them such a formidable asset.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: ATACMS missiles for HIMARS and MLRS
What is interesting about AGM-158 JASSM
The AGM-158 JASSM (Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile) is a modern precision-guided weapon with several distinctive features that make it both highly effective and strategically valuable.
The air-launched AGM-158 JASSM cruise missiles are equipped with an inertial guidance system enhanced by GPS correction, enabling them to strike targets with high precision, even in challenging environments.
The JASSM boasts impressive range capabilities, varying across its different variants. The standard JASSM has a range of up to 370 kilometers, while the upgraded JASSM-ER (Extended Range) extends this to approximately 980 kilometers.
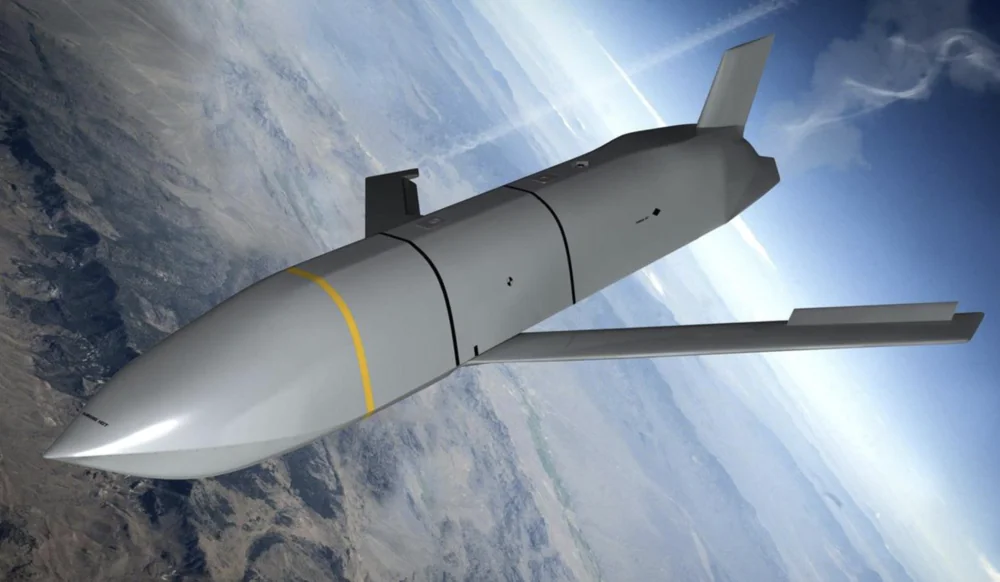

The AGM-158 features a stealth design that minimizes its radar visibility, making it significantly harder for adversaries to detect and intercept.
The missile is equipped with a 450 kg WDU-42/B warhead, enabling it to effectively destroy fortified targets, runways, ammunition depots, and similar objectives.
Additionally, the AGM-158 is highly versatile and can be integrated with various carrier aircraft, including the B-1B Lancer, B-52 Stratofortress, F-16, F/A-18, F-15E, and modern platforms like the F-35.

The missile is capable of operating in environments with active electronic warfare, thanks to its inertial guidance system, which functions independently of GPS signals.
The AGM-158 JASSM has the potential to become a critical tool for deterrence and defense. Its ability to strike targets deep behind enemy lines allows it to disrupt infrastructure, logistics, and command centers, significantly enhancing the combat capabilities of the deploying air force.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: V-BAT Vertical Takeoff UAV
History of AGM-158 JASSM creation
The development of the AGM-158 “Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile” began in 1995 at the request of the Pentagon. By the following year, the U.S. Air Force had officially launched the JASSM development program. In June 1996, McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing) and Lockheed Martin were awarded contracts for program definition and risk reduction, valued at $128 million and $110 million, respectively. Lockheed Martin ultimately won the competition, continuing the design process and commencing flight tests of the completed missile in 1999.
In November 1998, the U.S. Air Force awarded Lockheed Martin a $132.87 million contract for Engineering and Manufacturing Development (EMD) and full-scale production of the missile. Notably, this EMD contract with the Air Force was extended multiple times.
However, technical challenges emerged during the testing phase, necessitating refinements to the missile design. As a result, the program was delayed by several years. It wasn’t until the early 2000s that the AGM-158 met the required standards and was officially adopted into service with U.S. combat aviation units.
The first test of the AGM-158 JASSM at a range was successfully conducted in January 2001, with its operational capabilities demonstrated in April 2002.

Interestingly, around this time, work began on modernizing the missile to improve its core capabilities. This also led to the development of the AGM-158B JASSM-ER variant, which featured an extended range, followed by the anti-ship version, the AGM-158C LRASM.
The U.S. Air Force became the initial customer for the missile, with early contracts specifying the delivery of 4,900 missiles over an extended period. The U.S. Navy was also expected to place a significant order. However, there were concerns at one point about abandoning the AGM-158 program due to issues encountered during the testing phase. Lockheed Martin addressed these challenges, and as a result, deliveries were completed on time and in full.
The AGM-158 JASSM air-launched cruise missile has attracted interest from several countries. A significant number of missiles have been supplied to Australia, Poland, and Finland, with contracts also in place for deliveries to Germany, the Netherlands, and Japan.
According to recent reports, Ukraine may soon join the list of foreign operators, with deliveries potentially occurring in the coming months. Due to the special relationship with the U.S. administration, Ukraine could receive the missiles as part of aid before they are supplied to actual buyers.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: Precision-Guided AGM-154 JSOW Glide Bomb
AGM-158 JASSM variants
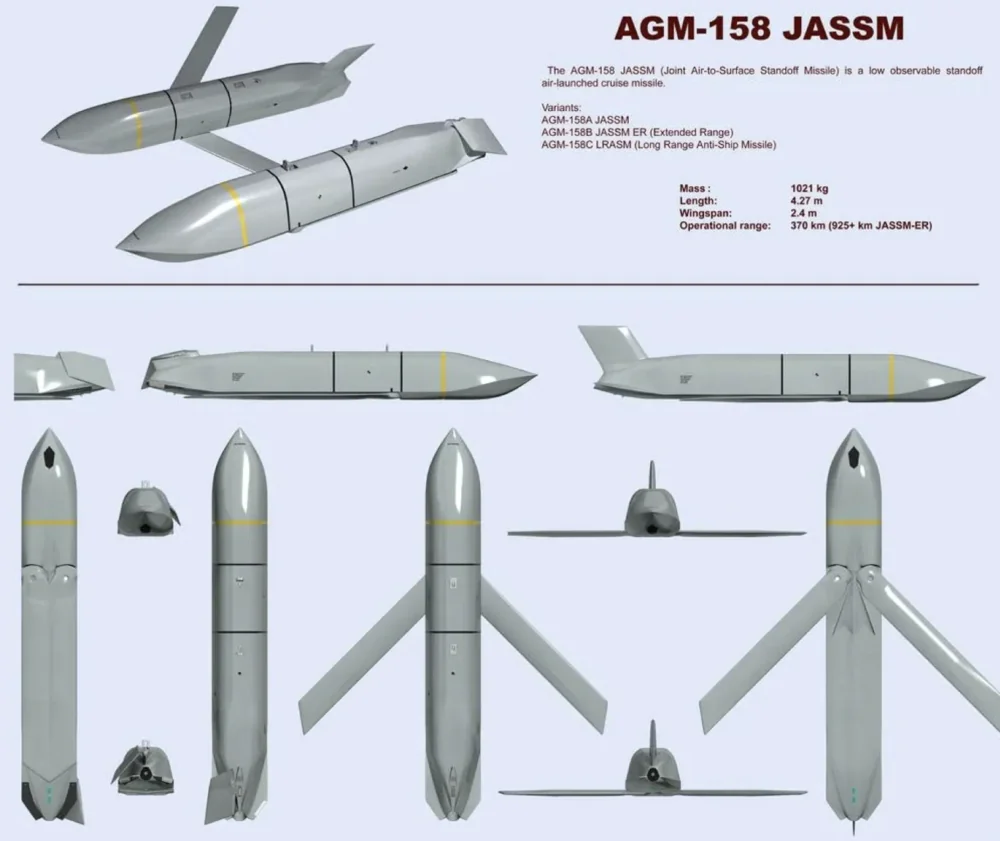
The AGM-158 JASSM cruise missile comes in several key variants, each designed for different missions and operational conditions. Here are the main versions:
- AGM-158A JASSM (base version) has a range of up to 370 km and weighs approximately 1,020 kg. Its warhead, the WDU-42/B, is a 450 kg fragmentation-explosive type. The missile uses an inertial navigation system (INS) with GPS correction. The first variant is designed for high-precision strikes against stationary targets. The AGM-158A JASSM features stealth technology to reduce its radar signature. This version is typically launched from strategic bombers (B-1B, B-52) as well as tactical fighter jets (F-16, F-15E).
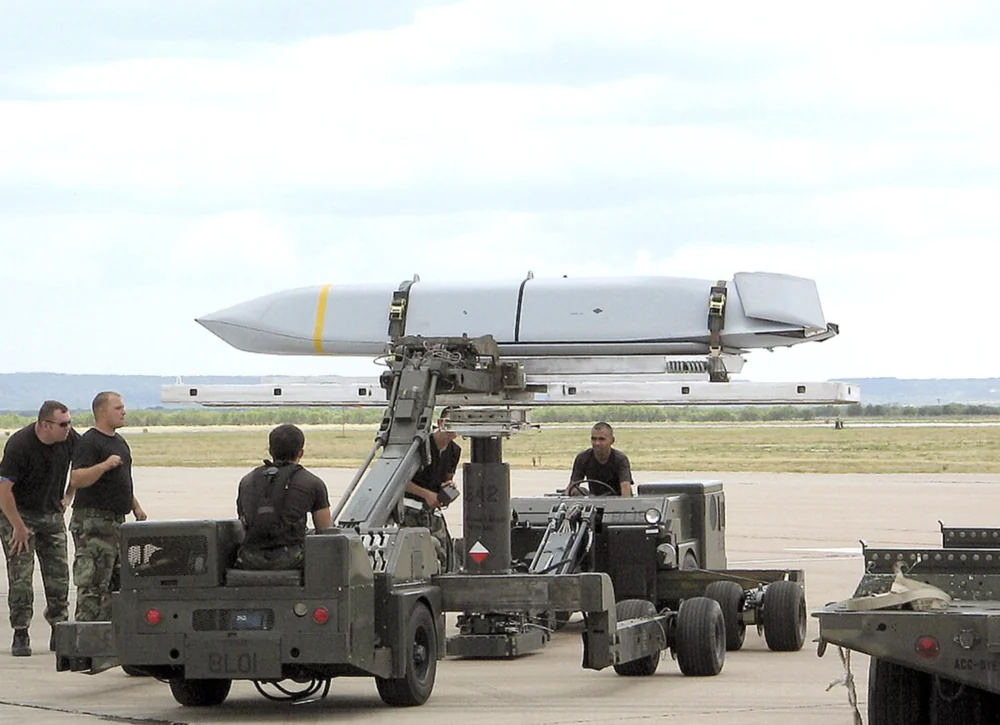

- AGM-158B JASSM-ER (Extended Range) is an upgraded version of the AGM-158A, weighing approximately 1,100 kg, thanks to a larger fuel tank compared to the base model. This increased size grants it an extended range of up to 980 km. The missile retains the same warhead as the basic version but has a refined navigation system, now incorporating an integrated, enhanced INS/GPS. The JASSM-ER also boasts improved autonomy in electronic warfare conditions, enhancing its operational capabilities in contested environments. The increased range enables missions beyond the reach of most air defense systems, allowing for strikes from a greater distance. Additionally, the missile is equipped with an upgraded engine and a larger fuel reserve. Most aircraft compatible with the base version, including the F-35, are also capable of deploying the JASSM-ER.
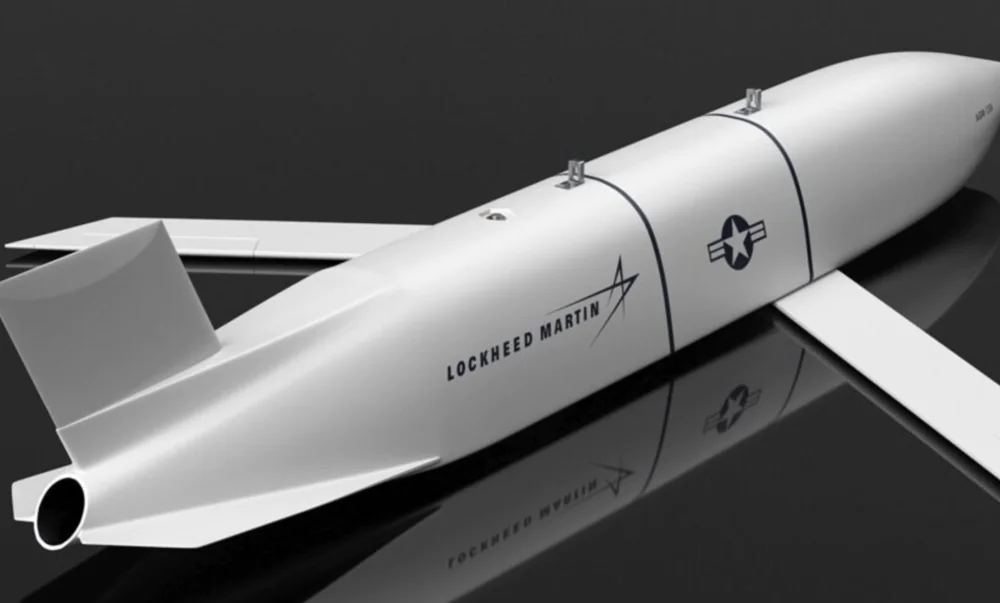

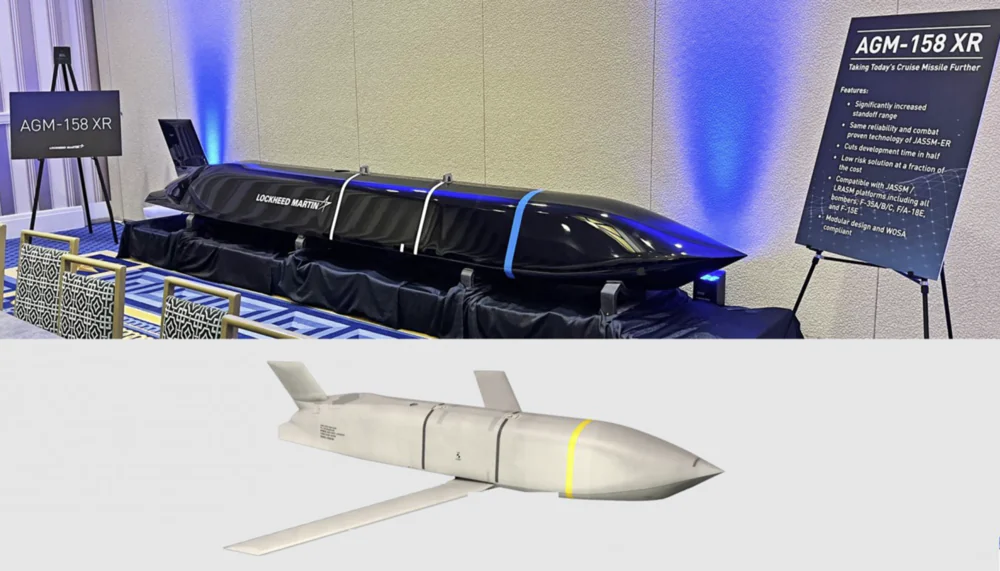
- AGM-158D JASSM-XR (Extreme Range) is the latest version of this cruise missile, still in development and refinement in certain aspects. What makes it noteworthy? First, its range has been significantly extended, now exceeding 1900 km. Despite this increase, the missile’s weight remains the same, just over 1100 kg. The warhead, the WDU-42/B, a 450 kg fragmentation-explosive type, remains unchanged. The new version of the missile is designed to target extremely distant strategic objectives. It incorporates advanced stealth technologies and a more efficient engine, making it suitable for strategic missions. The AGM-158D JASSM-XR also features the most modern inertial navigation system, enhanced with AI capabilities. This version of the missile is primarily deployed on strategic bombers.

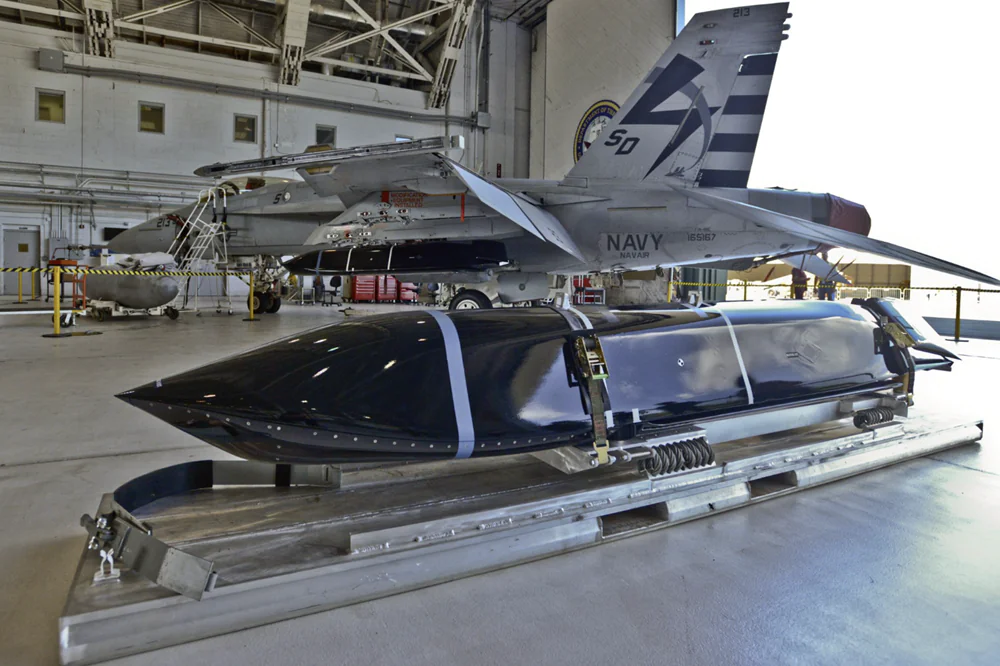
- AGM-158C LRASM (Long Range Anti-Ship Missile) is the anti-ship variant of the baseline air-launched cruise missile. Its range is close to 930 km. The missile features a multi-mode guidance system, which includes an active radar seeker (ARS) and passive sensors. It is designed to strike ships under challenging conditions, such as poor visibility and active electronic warfare (EW). The LRASM can be launched not only from aircraft like the B-1B, F/A-18E/F, and F-35 but also from ships and Mk-41 vertical launch systems.

- Hyper JASSM is a promising hypersonic version of the missile, currently under development. The goal of this project is to create a weapon capable of penetrating modern air defense systems. At this stage, the Hyper JASSM is still in the design and development phase.
Read also: Laser Weapons: History, Development, Potential, and Prospects
Design features of AGM-158 JASSM
The AGM-158 JASSM is an air-to-surface missile designed for use on both tactical and strategic aircraft. It is intended to target distant ground objectives, such as troop concentrations, command centers, and infrastructure.
The AGM-158 JASSM cruise missiles feature unique design characteristics that enhance their effectiveness, versatility, and survivability.
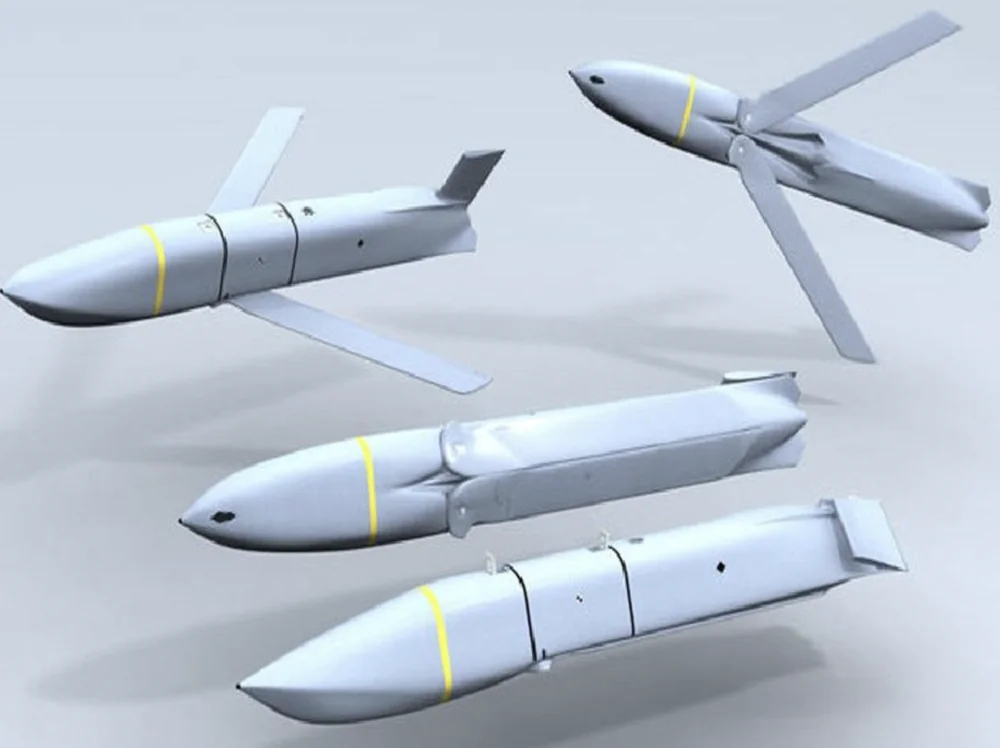

The missile is designed with a standard aerodynamic configuration. It features an elongated fuselage with an asymmetric cross-section, along with folding delta wings and tailfins. The folding wings reduce the missile’s size during transport and while being mounted on the aircraft. Upon launch, the wings deploy to ensure stable flight. The cruciform tailfins provide aerodynamic stability and are used for controlling the flight trajectory.
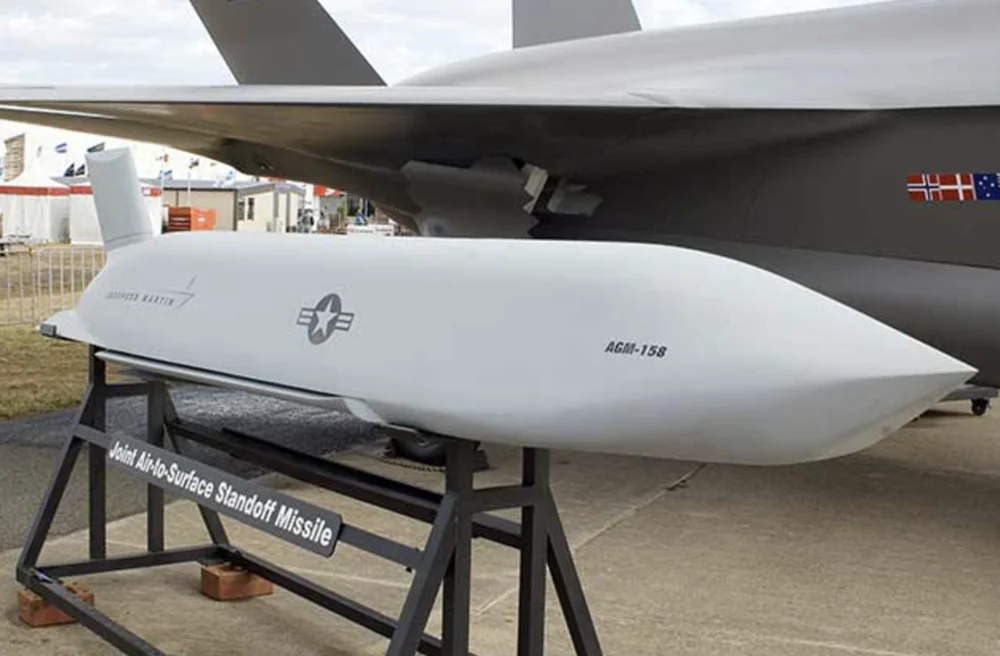

Stealth technologies were employed in the development of the AGM-158 JASSM, as evidenced by its distinctive appearance. The missile’s shape is optimized to reduce its radar signature. Additionally, materials that absorb radio waves are used to further minimize detectability.
The missile has a length of 4.3 meters, a fuselage width of 0.55 meters, and a wingspan of 2.7 meters. Its launch weight is 1021 kg, with 454 kg allocated to the warhead.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: LAV 6.0 ACSV Armored Personnel Carrier
The guidance and navigation functions of the AGM-158 JASSM are key to its effectiveness, ensuring precise targeting even in environments with intense electronic warfare.
A critical component is the inertial navigation system (INS), which uses gyroscopes and accelerometers to track the missile’s position in space. The main advantages of this system are its autonomy, as it does not rely on external signals, and its ability to operate effectively in GPS-denied environments.
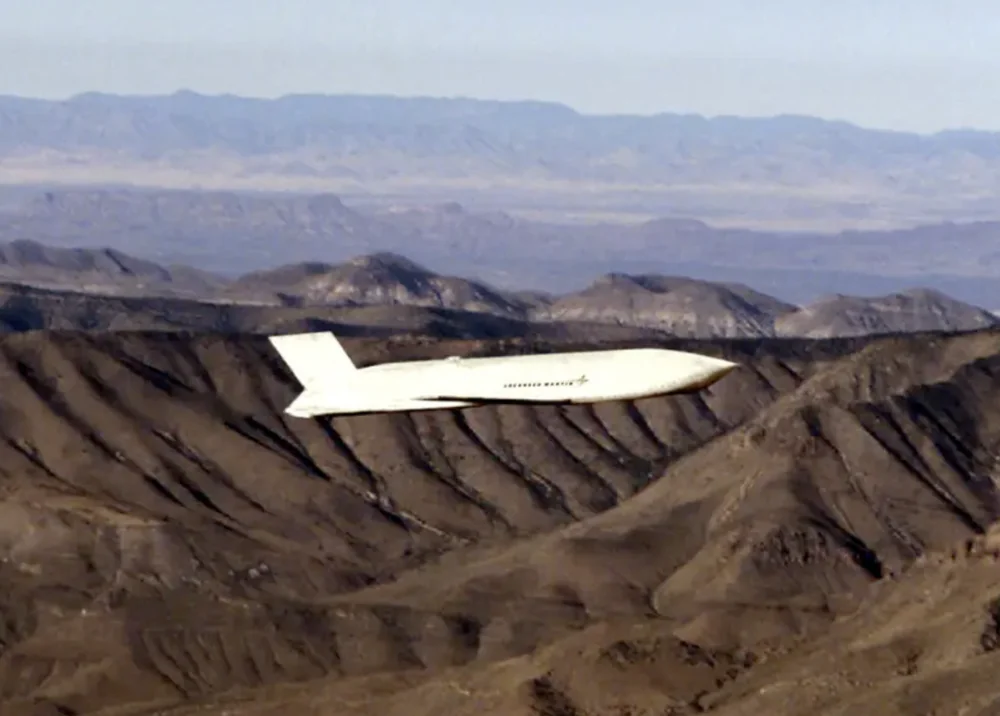

High-precision satellite navigation with GPS correction complements the INS, ensuring accurate targeting. It uses GPS signals to update the missile’s position during flight. A key feature of this system is its resistance to interference, provided by a secure military communication channel. It continues to function even in challenging environments with active electronic warfare systems. In the event of GPS/INS jamming, a backup system maintains navigation capabilities.
It is also worth mentioning the Terrain Contour Matching (TCM) system, which uses a pre-loaded terrain map. Sensors on the missile determine the altitude above the surface to adjust the flight path accordingly. This reduces the missile’s reliance on satellite navigation and enables it to fly at low altitudes to avoid radar detection.
The missile also features an onboard threat avoidance system, where artificial intelligence algorithms (in newer modifications) analyze the situation in real-time and automatically adjust the flight path to avoid enemy radar or missile engagement zones. This capability allows the missile to navigate through areas with dense air defense coverage, utilizing natural terrain features such as mountains, hills, and forests for cover.
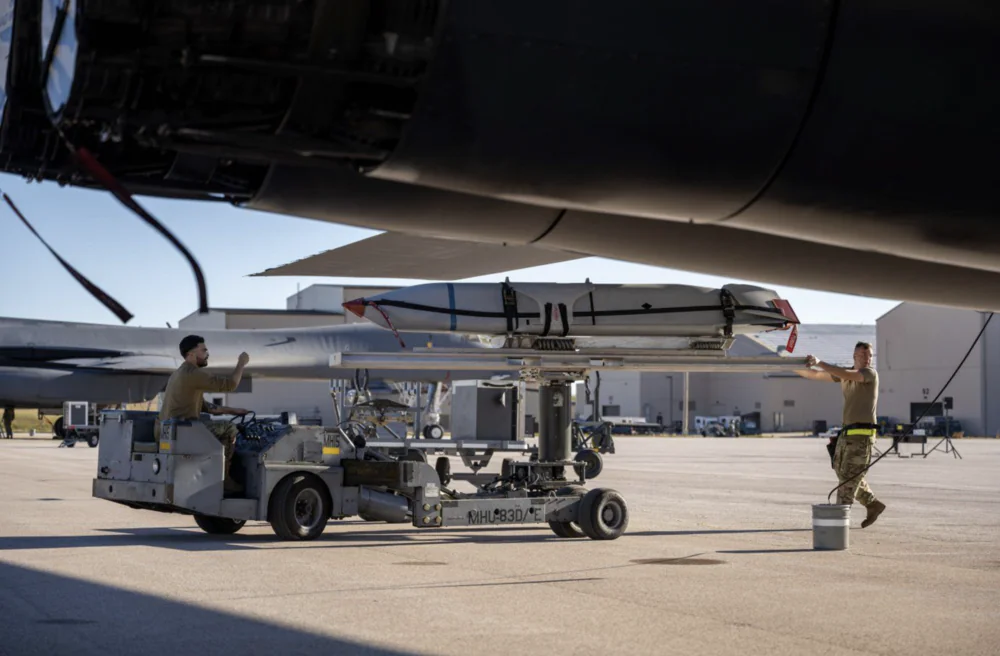

Thanks to its aerodynamic design, the missile can generate lift, which helps reduce fuel consumption. It flies at low altitudes to minimize the risk of radar detection. Prior to striking the target, the missile performs evasive maneuvers to avoid interception.
The target is entered before launch, and the missile’s route is calculated during the preparation phase. In versions with artificial intelligence, the missile can analyze the situation and change targets if necessary (for example, if the primary target is destroyed or otherwise unavailable).
In other words, the AGM-158 JASSM’s navigation system is designed with modern challenges in mind—GPS jamming, maneuvering air defenses, and complex battlefield conditions. The integration of INS, GPS, digital terrain mapping, obstacle avoidance, and automatic flight control ensures high accuracy, effectiveness, and survivability.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: Long-range AASM Hammer bombs
AGM-158 JASSM engines
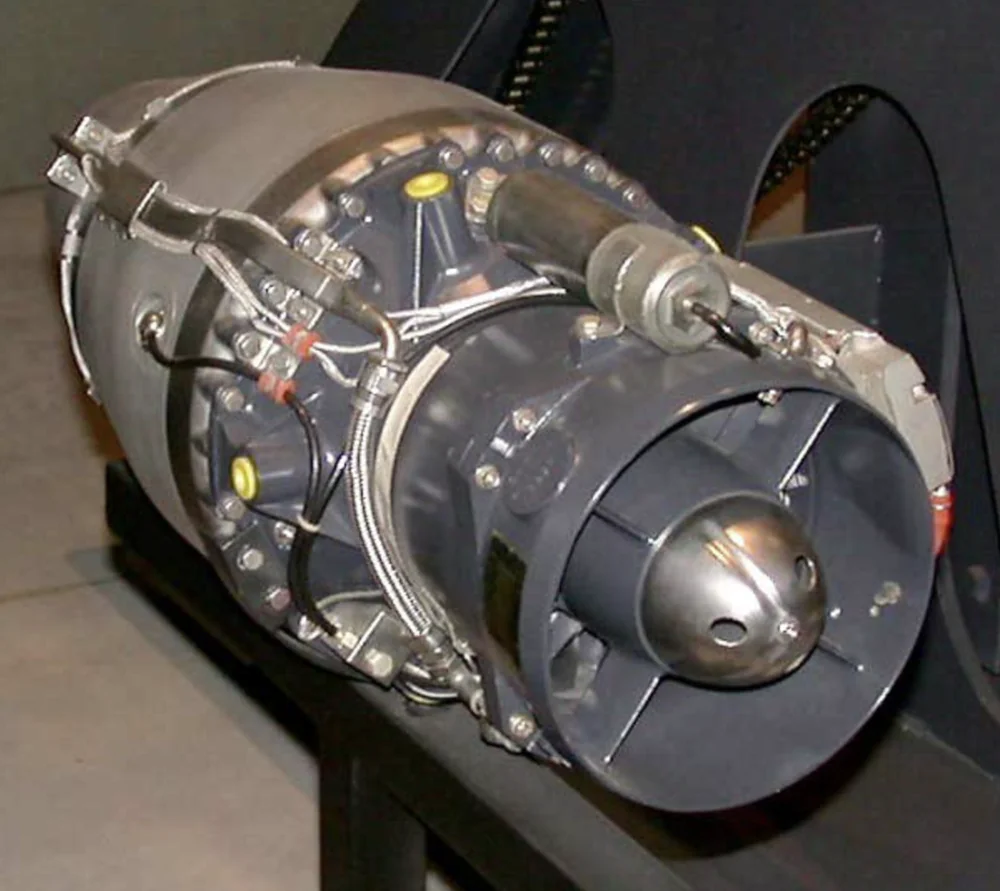
The standard version of the AGM-158 JASSM is equipped with the Teledyne J402-100 turbojet engine, which is an improved version of the original J402-CA-400 engine used in the Harpoon anti-ship missile, featuring a new compressor and fuel system. This compact and efficient engine provides optimal thrust for subsonic flight over long distances. The engine’s design minimizes infrared emissions, making it more difficult for thermal imaging systems to detect the missile.
The updated version, the AGM-158B JASSM-ER (Extended Range), is powered by the Williams International F107-WR-105 engine. This engine has been upgraded to increase the missile’s range to 980 km. The combination of the enhanced engine and a larger fuel tank significantly boosts efficiency. Additionally, fuel consumption has been reduced, optimizing the missile’s performance for extended subsonic flights.
For the AGM-158D JASSM-XR (Extreme Range) modification, which is still under development, rumors suggest that an improved engine is being designed. This new engine will offer enhanced efficiency when paired with next-generation fuel tanks, enabling a flight range of over 1900 km. Further optimization of fuel consumption will make it suitable for conducting strategic missions.
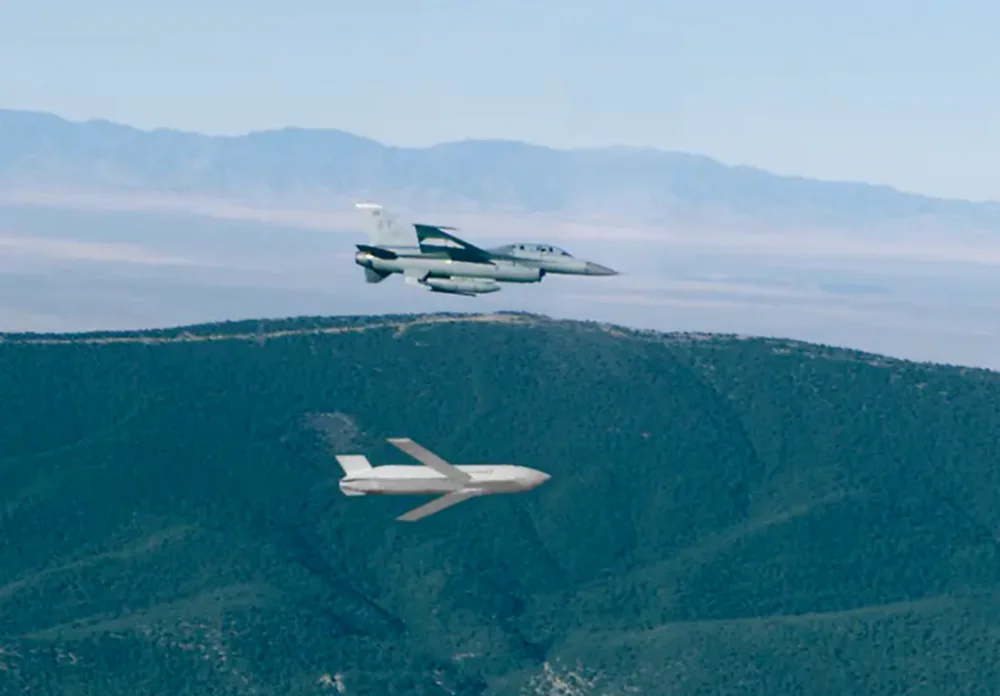

The missile travels at subsonic speeds (approximately 0.7–0.9 Mach), which helps conserve fuel and allows it to fly at low altitudes, minimizing the risk of detection. The reduced noise level during engine operation makes it more difficult for acoustic detection systems to track the missile.
The engines are designed to perform in challenging conditions, including high humidity, low temperatures, and strong turbulence.
Research on the creation of Hyper JASSM considers the integration of hypersonic engines that can provide a breakthrough for modern air defense systems. This will significantly expand the missile’s capabilities by increasing its speed to hypersonic.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian victory: Skynex anti-aircraft artillery systems from Rheinmetall
Warhead of the AGM-158 JASSM cruise missile
The warhead of the AGM-158 JASSM cruise missile is designed to meet the requirements for highly accurate targeting of critical objectives. It combines high power, adaptability, and stealth features. The WDU-42/B is a standardized high-explosive fragmentation warhead used across all AGM-158 JASSM variants, with a weight of 450 kg.
The WDU-42/B warhead is intended for the destruction of stationary, fortified, and strategically important targets, such as bunkers, command centers, storage facilities, and airfields.
The single-component warhead includes an explosive charge and a casing designed to withstand high shock loads. High-strength steel or other durable alloys are used to enhance penetration into fortified structures. The missile is equipped with a specially developed high-powered charge that creates a powerful shockwave, maximizing its effectiveness in destroying reinforced targets.
The Height of Burst (HOB) system allows the warhead’s detonation altitude to be programmed for maximum effectiveness based on the target type. It operates in two modes: ground burst for targeting fortified structures and airburst for maximizing damage to open areas. This flexibility enables the AGM-158 JASSM to adapt to various mission requirements, enhancing its versatility in different combat scenarios.
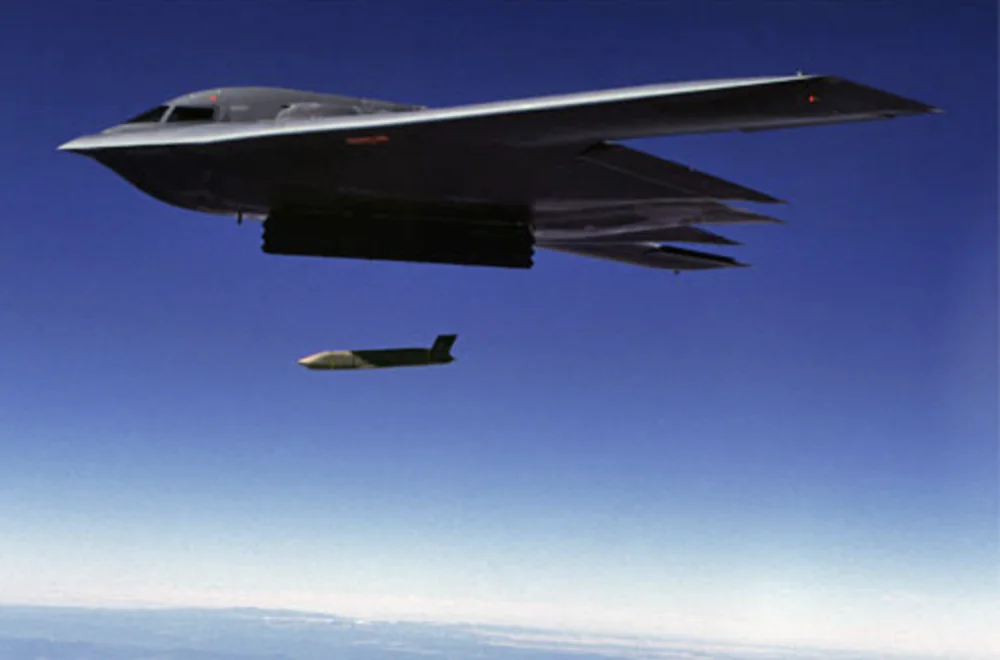

The warhead is equipped with a multifunctional detonator, such as an electronic detonator, which provides high reliability and flexibility in adjustments for different missions. This makes the warhead suitable for targeting a wide range of objectives, including enemy strategic assets, infrastructure, large buildings, and other critical targets. The precision of the AGM-158 JASSM is remarkable, with a minimal target accuracy error of only 3 meters, ensuring high effectiveness in hitting critical points.

The WDU-42/B warhead for the AGM-158 JASSM is a versatile payload capable of delivering high effectiveness against a wide range of targets. Its power, penetration capability, and precision make this missile a critical component in modern military operations.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: UAV Primoco One 150
How will AGM-158 JASSM be useful for Ukraine
The AGM-158 JASSM cruise missile could be extremely valuable for Ukraine in the context of modern warfare due to its technical capabilities and features. Its long range (370–1900 km) enables the targeting of strategically important objectives deep within enemy territory, such as command posts, logistics hubs, ammunition and fuel depots, and energy infrastructure supporting the enemy’s military operations. For example, it could be used to strike targets in Crimea, Donbas, or other occupied regions. This capability would enhance Ukraine’s ability to disrupt enemy operations, weaken their logistical capabilities, and target critical infrastructure from a safe distance, thereby improving overall strategic flexibility and operational effectiveness.
The AGM-158 JASSM is designed to avoid radar detection, making it highly effective against advanced enemy air defense systems like the S-300 or S-400. The missile is capable of flying at extremely low altitudes, staying under radar detection thresholds, which significantly enhances its survivability and ability to strike critical targets deep within enemy territory.
The explosion can be programmed for either bunker penetration or surface damage, allowing the missile to effectively destroy hardened targets such as bunkers, depots, or key bridges used by the enemy. With a targeting accuracy of up to 3 meters, it ensures precise strikes with minimal collateral damage, making it a highly efficient and reliable weapon for strategic operations.
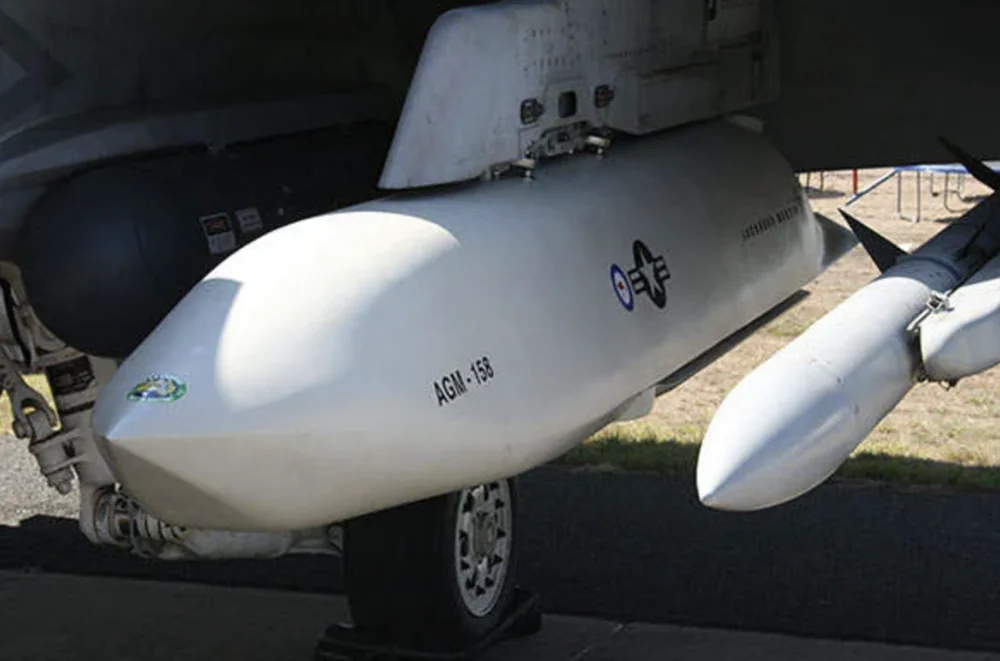

The JASSM missiles provide Ukraine with the ability to strike critical targets without entering the enemy’s air defense zone. This increases the survivability of carrier aircraft such as the MiG-29 and Su-27, which can be adapted to launch the missiles. Additionally, it’s worth noting that F-16s, which are already in service with the Ukrainian Air Force, can also be used for this purpose.
We believe in our Armed Forces, and we are confident that they will be able to break the backbone of the orc hordes from Moscow. Victory will be ours! Glory to Ukraine!
And if you are interested in articles and news about aviation and space technology, we invite you to our new project AERONAUT.media.
Read also:
- Weapons of Ukrainian Victory: Depleted uranium munitions
- Weapons of Ukrainian victory: 155 mm Vulcano guided artillery shell

