© ROOT-NATION.com - Use of content is permitted with a backlink.
The legendary FIM-92 Stinger portable anti-aircraft missile system helps our Armed Forces of Ukraine to effectively fight against airborne threats and other russian fascist targets.
FIM-92 Stinger missiles belong to the category of MPADS. Light, mobile, they can be operated by even one person (or formally two), they are extremely effective and dangerous weapons in the fight against enemy aircraft. These complexes were first used during the Falklands War, but became widely known thanks to the Taliban, which used them to shoot down Soviet aircraft. Thus was born the legend – the FIM-92 Stinger.
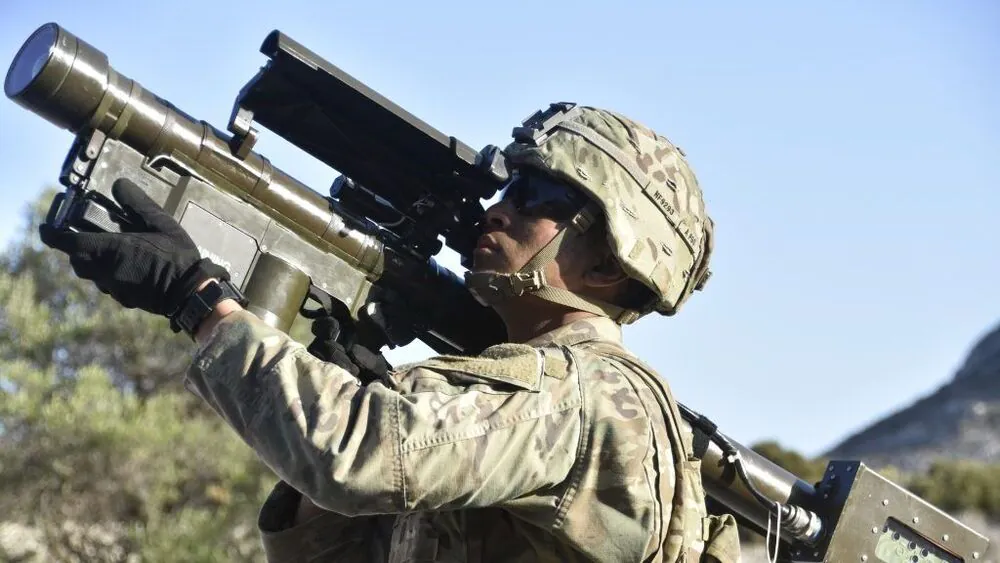

Read also: Who are Anonymous? History and present
Who produces FIM-92 Stinger?
FIM-92 Stinger was developed and manufactured by General Dynamics of the United States. This is the same corporation that now produces the M1A2 Abrams tanks, which are in service with the United States and its NATO partners. Currently, Raytheon is responsible for the production of missiles.

The Stinger rocket engine was developed by Aerojet Rocketdyne, a well-known rocket engine company. There have even been rumors that the company is about to be bought by an American arms giant Lockheed Martin, which supplies F-35 aircraft. However, in February this year, the agreement was canceled due to restrictions by the local market regulator.
Read also: Invasion of Ukraine: Bayraktar TB2 strike UAV review
What’s inside Stinger missile?
The FIM-92 Stinger missile itself consists of several basic elements: a section with a homing head in front of the missile, a warhead, a propulsion section and a control section.
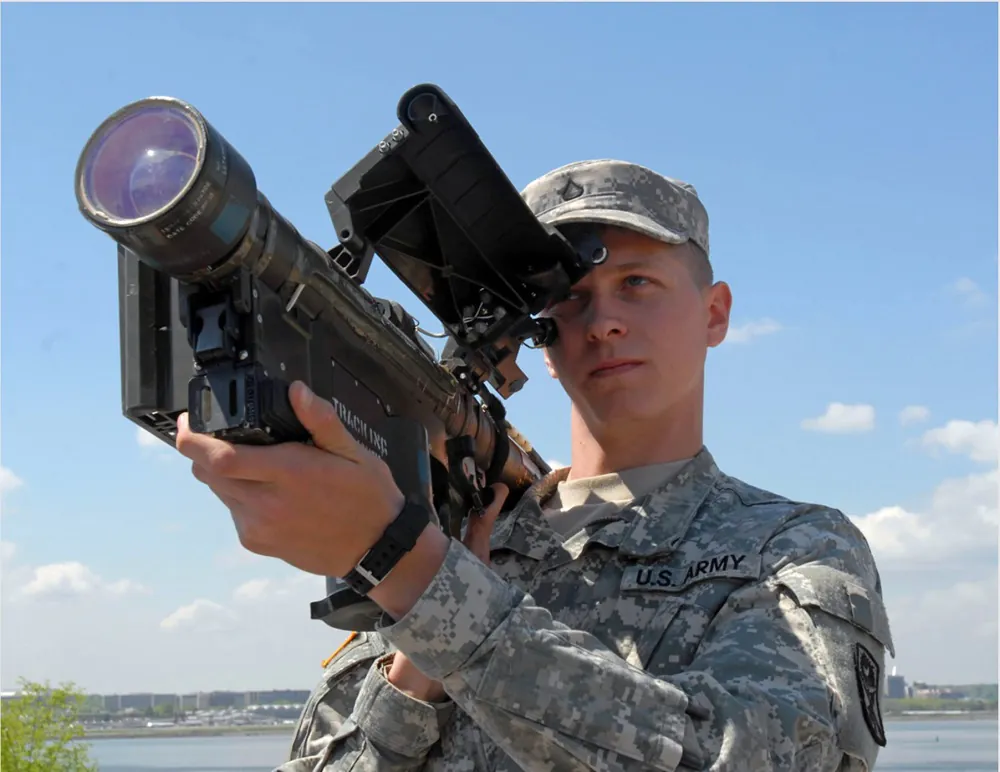

Two engines are used to launch the rocket. Launcher, a small rocket engine allows the rocket to leave the container in which it is stored, and move away to a safe distance from the operator. Then comes the main two-stage Stinger propulsion engine to accelerate the missile to its cruising speed and support it throughout the flight.

The FIM-92 Stinger launcher includes an operator’s handle and a trigger, as well as ‘friend-or-foe’ recognition system and a so-called BCU, or battery coolant unit. This ensures that the homing head will be cooled immediately before take-off and the entire system will receive the necessary energy. If it does not switch on within 45 seconds, the operator must replace the BCU with a new one.
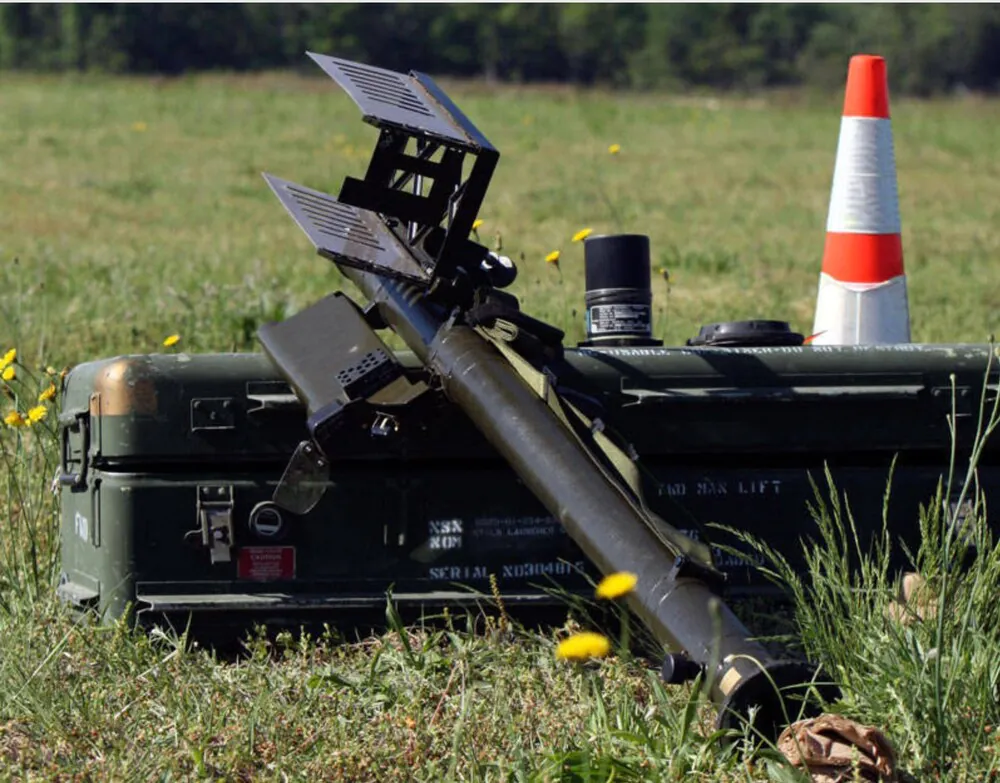

What was FIM-92 Stinger made for?
As you can guess, FIM-92 Stinger missiles were developed as a successor to previously used systems of this type. After the significant success of the FIM-43 Redeye, General Dynamics decided to improve its product and develop a new, improved hand-held surface-to-air missile.
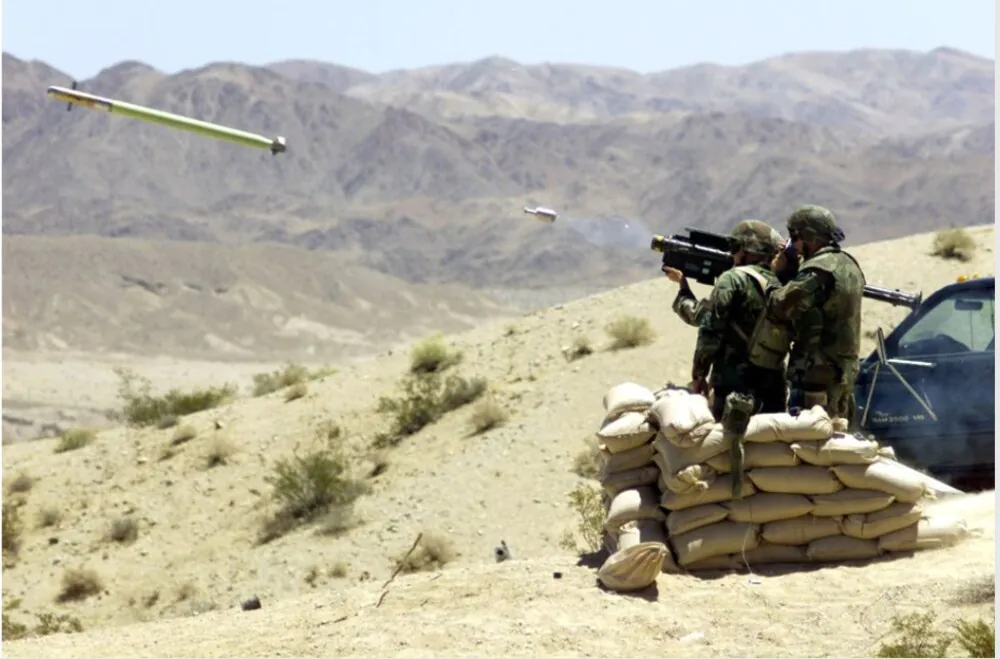

Portable missile systems are the lowest level of air defense, and in the case of infantry, they are basically the last resort to help destroy not only the enemy’s manpower, but also its support vehicles. The light weight of the whole complex allows one soldier to carry it and use it at a critical moment for the military unit.
The FIM-92 Stinger missile, launched at the right moment by a properly trained operator, is actually very difficult to counter even by modern aircraft. If the operator attacks, for example, a helicopter and does so from a relatively close distance, the crew of such an aircraft has almost no chance, because the protection systems installed on board will have very little time to react. Stingers are especially useful in advanced positions or during maneuver warfare, when the main air defense systems are insufficient, or they were not deployed in time.
Read also: Switchblade: American kamikaze drones to protect Ukraine
Where are FIM-92 Stinger missiles used beside portable launchers?
It would seem that the FIM-92 Stinger is a portable launcher and there should not be any other options for launching these missiles, but it’s not that in this situation. High efficiency of these rockets has led to the creation of a wide range of modernized military systems equipped with these missiles.
I think many of you have heard of high-mobility multi-purpose wheeled vehicles, the so-called HMMWV, which have found application in the civilian market as well as in the military. This includes a combat vehicle with 8 FIM-92 Stinger missile launchers, called the M1097 Avenger air defense system.
Another vehicle that employs Stingers is the Bradley Linebacker, a vehicle based on the Bradley chassis and designed as a SHORAD (short-range air defense) unit.
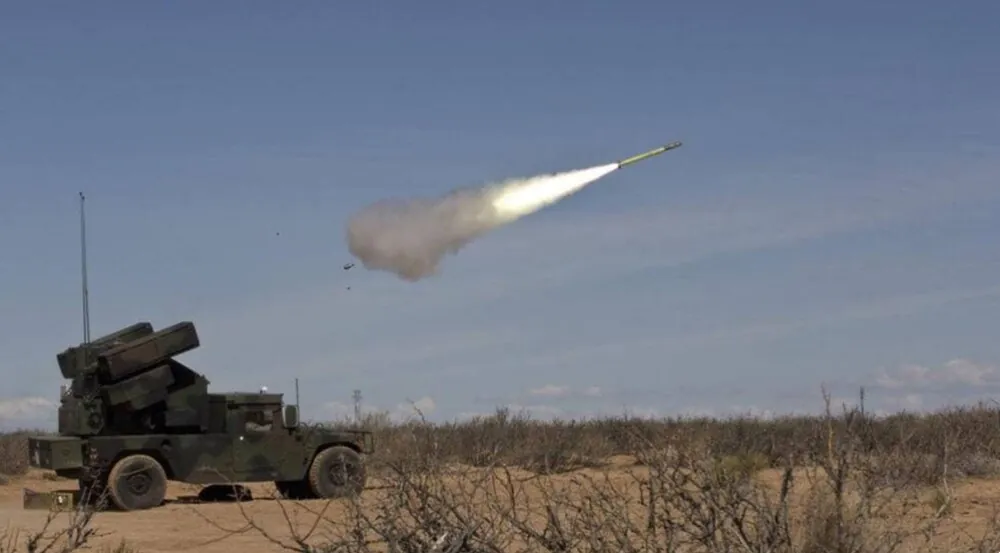

A similar LAV-AD light armored air defense vehicle used by the US Marine Corps serves for similar tasks as Bradley Linebacker.
FIM-92 Stinger missiles can also be used as combat equipment for aircraft. The Kiowa Warrior (OH-58D) helicopters equipped with these missiles are no longer used by the US military, but have been an important part of the United States military for a long time. Among the combat helicopters that are constantly used and equipped with Stingers, we can name the AH-64, which even in the latest ‘E’ version still uses this proven and reliable design. Finally, we can mention the MH-60 helicopters used by US Special Forces, which are also equipped with FIM-92 Stinger missile systems.
It is also worth mentioning as the armament for drones. One of the predecessors of combat drones, MQ-Predator, in addition to Hellfire missiles, was also equipped with FIM-92 Stinger missiles, adapted to launch from the air.
In addition to American platforms, Stingers have also been integrated with such vehicles as the Eurocopter Tiger and Turkish T129 ATAK helicopters.

Read also: Best video games developed in Ukraine
How does FIM-92 Stinger missile work?
As it was already mentioned, the FIM-92 Stinger is usually a surface-to-air missile, which belongs to the passive class of missiles. The infrared head used on the projectile is able to capture the heat source to which the operator directs it. After firing, the missile moves to the captured object, aiming at the specified source of heat radiation. Because Stingers are fired shoot mainly at airplanes and helicopters, the source of heat of which is the engine, or the exhaust injectors of the engines in particular, because that’s where a lot of heat energy is released directly into the atmosphere. This greatly facilitates the operation of the missile system.
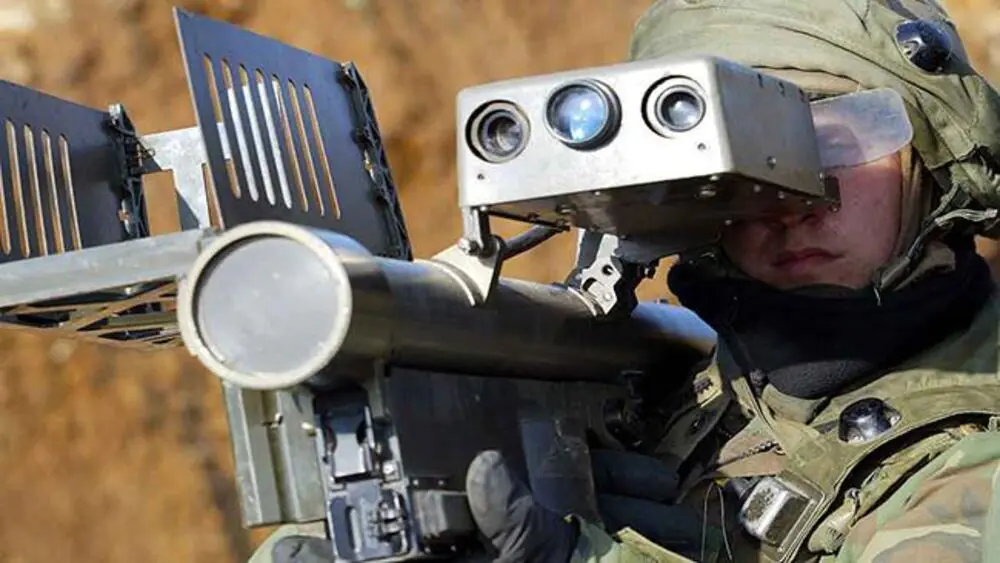

The Stinger system is passive, as mentioned above, thus it itself has no radiation that could be captured by the onboard protection systems of the aircraft or helicopter. This is a ‘fire-and-firget’ system – thanks to this, the operator only has to lock the target, launch a missile and can immediately proceed to further action, because the missile will do the rest on its own.
In order to avoid friendly fire, FIM-92 Stinger missiles are able to communicate with aircraft’s friend-or-foe systems, and before firing, the operator already knows whether he is dealing with friendly or an enemy vehicle. An effective control system can correctly calculate the trajectory of a missile, which helps to hit a moving maneuvering target. Russian MiG, SU and TU aircraft’s signatures have ‘special’ status, which makes them almost automatically recognized by the missile system as foe.
In the last stage of reaching the target, the system software shifts the aiming point from the heat source closer to the center of the target to maximize the effectiveness of a relatively small warhead.
Read also: Best music to come out of Ukraine: Famous rockers, Eurovision darlings, and everything in-between
How does the whole process look like step-by-step?
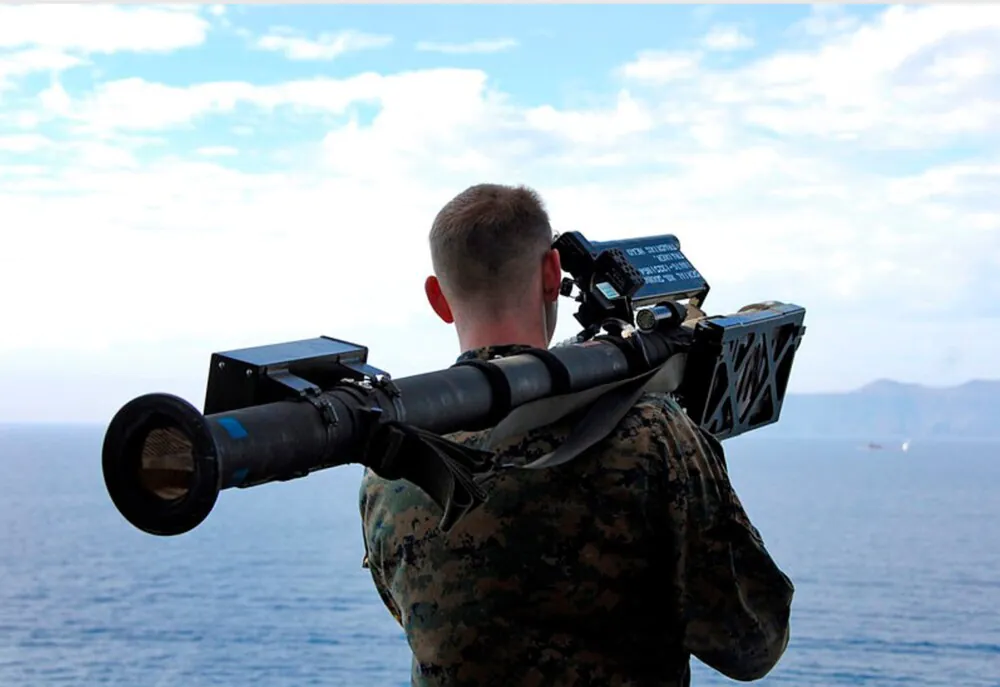

The operator prepares Stinger for action. When he finds the target and is convinced that it is an enemy aircraft, he pulls the trigger. Then the above-mentioned first auxiliary engine fires off, which forces the rocket to leave the launcher tube, and when the main engine ignites, it falls off. This is a solid propellant rocket launcher. After starting, the Stinger accelerates to the target speed, and then the engine maintains it, slowing down the system’s thrust. After hitting the target detonation occurs (impact or non-contact ignition in new models). If the missile does not reach the target, it self-destructs after a certain period of time. Self-destruction is an effective function to counter the capture of the warhead by the enemy.

Stinger missile modifications
Modifications of the FIM-92 Stinger missile are still being developed, although their service life has expired. The United States is currently working on a successor to this type of missile. In the latest version, introduced in 2019, the Stingers received a proximity fuse that allows them to hit smaller targets such as drones. This is not an isolated concept, as a similar working model has also been used for APKWS missiles.
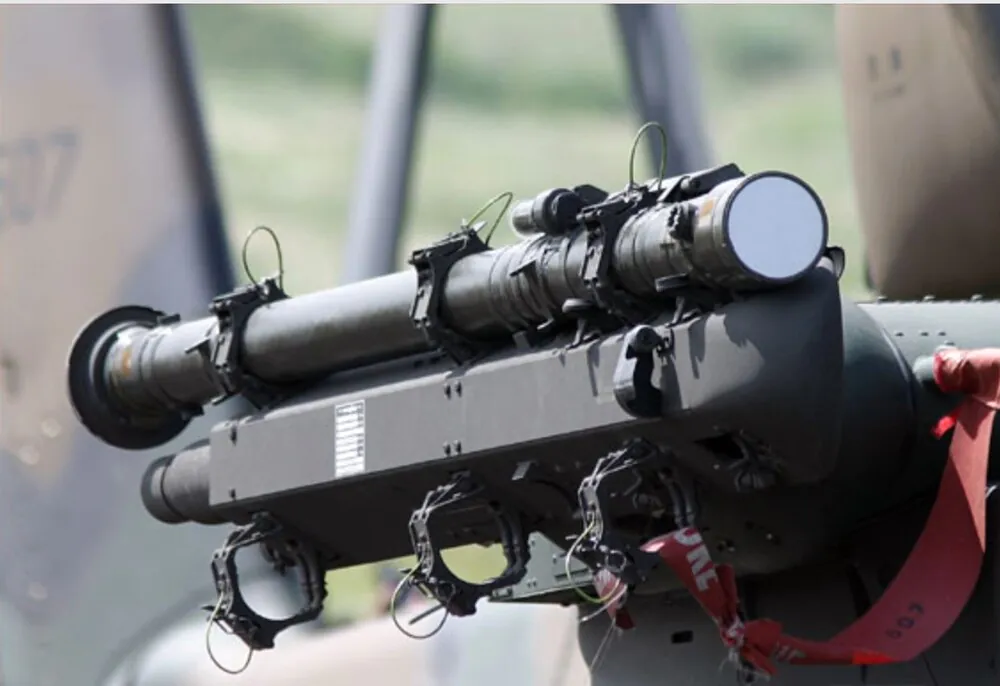
The basic version of the Stinger is version A, which uses a passive infrared air target finder, however, it can be misled by thermal traps (torches). Therefore, in version B, it was changed to an IR / UV system, which was more difficult to deceive. In version C, the resistance to attempts to deceive the guidance system was further improved, and there was also the ability to quickly download new software. This allowed to update the data on known countermeasures. In modification D, the fight against enemy deterrence systems was further developed. Modification E improves the flight behavior of the projectile and its effectiveness against small targets. Modification F was a further development of modification E, bringing the improvements already made to an even higher level. The Ukrainian Armed Forces received the FIM-92 Stinger in the penultimate version of E, which proved its effectiveness in combat, successfully destroying enemy aircraft and helicopters. Sometimes it seems that russian pilots are afraid of the FIM-92 Stinger anti-aircraft system at the genetic level, so russia has even made threats and warnings to the United States over the supply of the famous anti-aircraft missile system to Ukraine. This clearly gives reason to say that russians are afraid of the Stingers.
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian victory: ATGM Javelin FGM-148 – ruthless to enemy tanks
Specifications of FIM-92 Stinger
- Length: 1.5 m (5′)
- Diameter: 7 cm (2.75″)
- Projectile weight: 10 kg (22 pounds)
- Launcher and projectile weight: 15.2 kg (34.5 pounds)
- Warhead weight: 3 kg (6.6 pounds), including 1kg of HTA-3
- Effective range: 4-8 km
- Maximum engagement altitude: around 3 km
FIM-92 Stinger operation manual
The Ministry of Defense has even posted a video instruction on the use of FIM-92 Stinger. Therefore, everyone will be able to master the operation of this legendary anti-aircraft missile system.


Good luck hunting orcs!
Why are FIM-92 Stinger shipments important to us?
There was a lot of talk before and now during the war, do we need FIM-92 Stingers? We definitely do. We all understand that the occupants have an advantage in the air, which allows them, sometimes with impunity, to bomb our towns and villages, bring in troops with the help of helicopters and provide fire support to infantry.
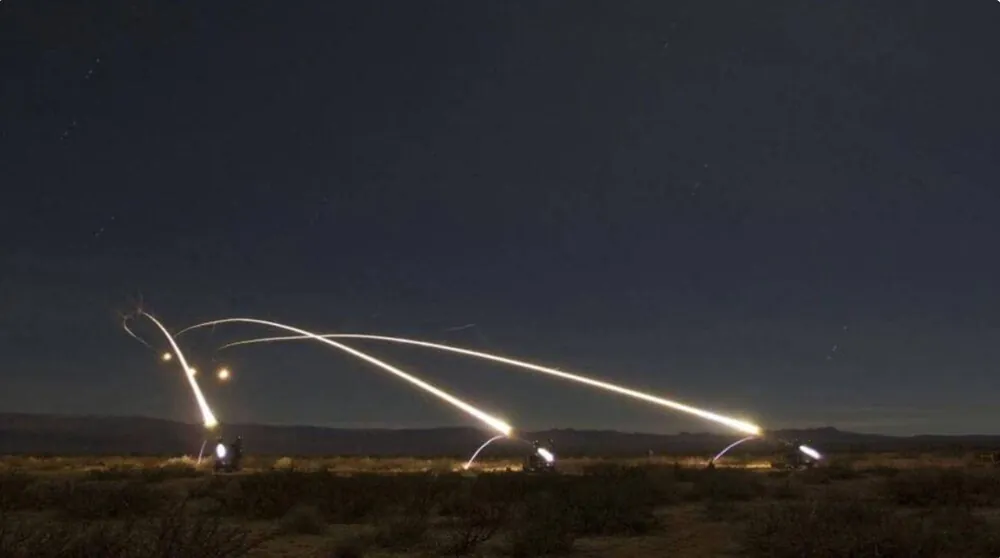

But the deployment of the Stingers changed this situation. Every day we hear about downed planes and helicopters. I’m sure most of them were hit with FIM-92 Stinger MPADS. The enemy must watch their backs even in the air and wait for a powerful shot.
Burn in hell, invaders! Everything will be Ukraine! Glory to Ukraine!
Read also: Weapons of Ukrainian victory: ATGM Stugna-P – russian tanks are in trouble
You can also help Ukraine fight with Russian occupants via Savelife or via an official page of the National Bank of Ukraine.

