© ROOT-NATION.com - Use of content is permitted with a backlink.
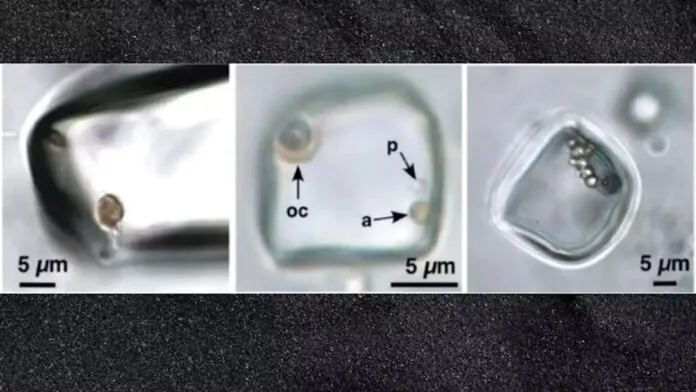
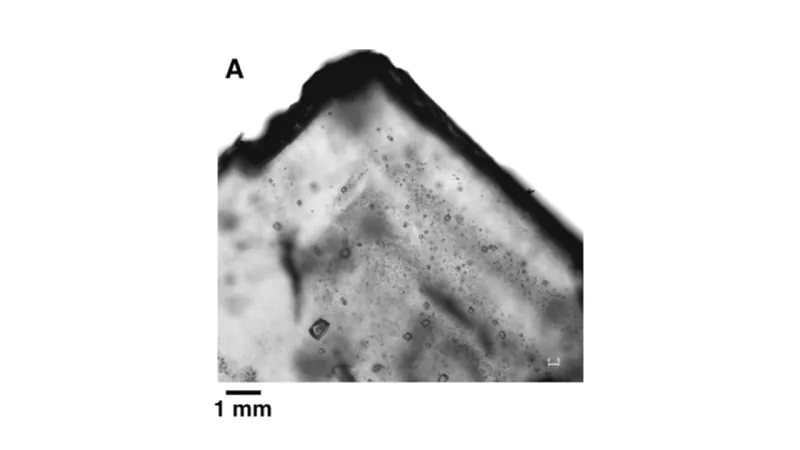
In central Australia, scientists conducted a study of saline sediments to find ancient microorganisms. To do this, they have studied halite from the Brown Formation in Australia, which preserved the ancient, salt-rich landscape. Scientists took samples of halite from depths between 1481 and 1520 m, then conducted a microscopic study using both visible and ultraviolet light, increasing the content of liquid salt pockets inside up to 2000 times and focusing on primary crystals formed 830 million years ago.
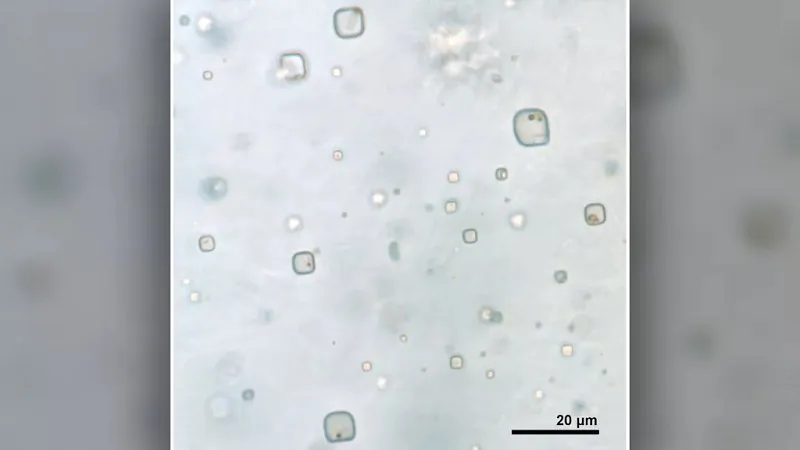
In addition, researchers found eukaryotes (algae and fungi with clear cell nuclei) and prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea without nuclei). According to scientists, they were able to distinguish these organisms by shape, size, color and fluorescence in ultraviolet light. Researchers cannot determine the exact species of these microorganisms, although one of them is very similar to Dunaliella, which was found in both ancient and modern saline environments. Organisms are tiny, 0.5-5 microns in diameter (for comparison, human hair is about 70 microns thick).
Salt-loving microorganisms are those that are able to hibernate or otherwise change their metabolism to stay alive when the water around them dries. In the year 2000, scientists said they had revived a 250-million-year-old bacterium from salt, although they could not conclusively prove that their zombie bacteria were not modern contaminants. In another scientific work, 101.5 million-year-old bacteria were revived from bottom sediments.

Researchers have not yet uncovered the crystals to determine if Australian microbes have a chance for a second life. The finds can be used to search for ancient “aliens”. The rocks of the Brown formation were formed in an environment similar to the environment that probably existed on ancient Mars. The methods the team used to study these organisms can also be used to search for long-extinct microorganisms from the Red Planet. The Perseverance rover collects rocks that will eventually be delivered to Earth, and non-destructive research methods will be needed to understand the context of these formations. Which are now developed based on terrestrial samples. The most interesting thing is that, according to scientists, the found organisms can be revived, but whether it is necessary or not – they can’t say.
You can also help Ukraine fight with Russian occupants via Savelife or via an official page of the National Bank of Ukraine.
Read also:
- New solar cells can generate energy at night
- NASA will shut down the InSight martian probe this year